Hailong Yan,
Yu Wang,
Mengyao Wu,
Yuying Li *,
Wanping Wang,
Dongliang Zhang,
Jingjing Guo,
Nicola Fohrer, and
Bailian Larry Li
. Feeding Behavior and Ecological Significance of Craspedacusta sowerbii in a Freshwater Reservoir: Insights from Prey Composition and Trophic Interactions. Biology 2025, 14(6), 665; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14060665
Abstract :
This study investigates the feeding behavior and ecological role of Craspedacusta sowerbii in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, a crucial freshwater source in central China. Through in situ cultivation, microscopic examination, and amplicon sequencing analysis, we identified the primary food sources of C. sowerbii within the reservoir’s aquatic food web. Our results indicate that C. sowerbii predominantly consumes zooplankton, specifically rotifers, copepods, and cladocerans, while phytoplankton is ingested less frequently and often remains undigested. Amplicon sequencing data further confirms that the prey composition of C. sowerbii is enriched in zooplanktonic communities compared to phytoplanktonic communities. Our findings suggest that C. sowerbii plays a significant role in regulating plankton populations and shaping the planktonic community structure in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, thereby contributing to the ecosystem’s functions and trophic dynamics. This study enhances our understanding of the feeding ecology of C. sowerbii and highlights its potential as a bioindicator species for assessing freshwater ecosystem health and monitoring water quality.
Keywords:
Craspedacusta sowerbii ; Danjiangkou Reservoir ; feeding behavior ; ecological role ; aquatic food webs
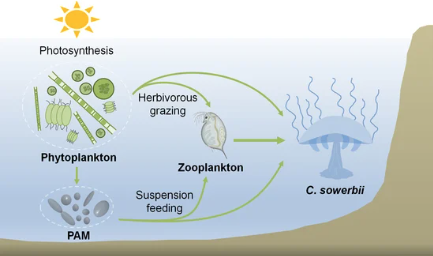
Figure 1.
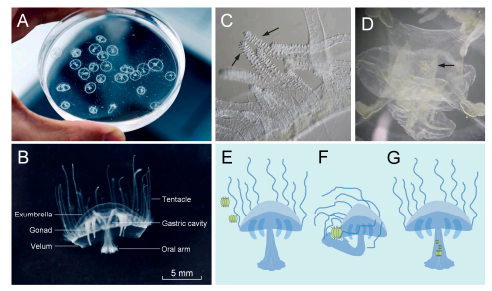
Figure 2.
Behavioral observations of live
C. sowerbii
specimens. (
A
,
B
) In situ behavioral observations
of
C. sowerbii
. (
C
) Tentacles of
C. sowerbii
(arrows). (
D
) The suspected prey in the gastric cavity of
C. sowerbii
(arrow). (
E
) Phytoplankton approached the tentacles of
C. sowerbii
. (
F
)
C. sowerbii
grasped
the phytoplankton by curling its tentacles and simultaneously bending its oral arm to envelop the
prey. (
G
) Phytoplankton stored in the gastric cavity of
C. sowerbii
.
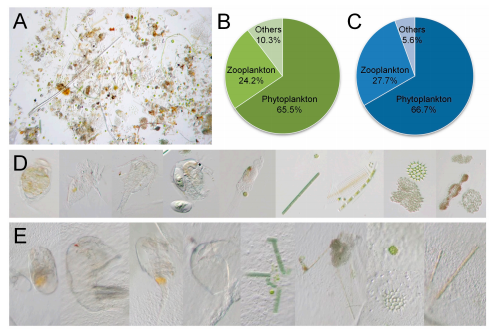
Figure 3.
The environmental species community and food composition of
C. sowerbii
. (
A
) Concen
trated water sample of the Danjiangkou Reservoir. (
B
) Percentage of the environmental species
community. (
C
) Percentage of the species community in the gastric cavity of
C. sowerbii
. (
D
) Typical
environmental species observed under a microscope. (
E
) Typical species community observed within
the gastric cavity of
C. sowerbii
.
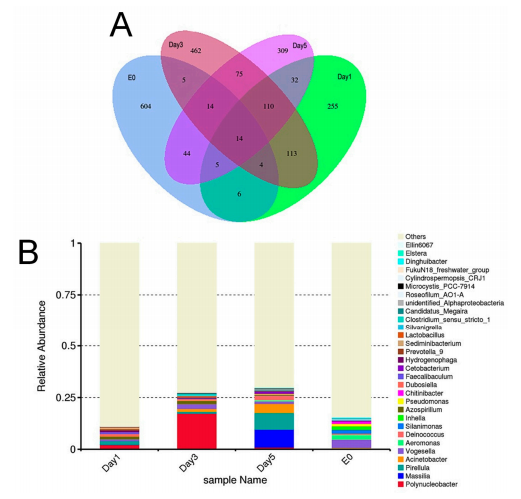
Figure 4.
16S amplicon sequencing analysis comparing environmental samples with
C. sowerbii
samples. (
A
) Venn diagram analysis of the ASVs via 16S amplicon sequencing. (
B
) Bar plot showing
the relative abundance of the top 30 genera identified via 16S amplicon sequencing.
Biology期刊
Biology期刊的最新影响因子为4.2,5年影响因子为4.4,CiteScore为4.0。ISSN 2079-7737,涵盖植物学、动物学、微生物学等所有生物领域。2011年创刊,2014年被PubMed和Scopus收录,2019年进入SCIE,2020年首次获得影响因子(3.796)。